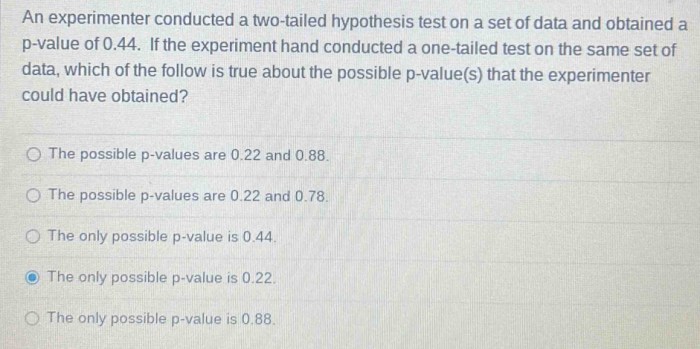
An experimenter conducted a two tailed hypothesis – An experimenter conducted a two-tailed hypothesis, delving into the intricacies of scientific research, hypothesis formulation, and experimental design. This comprehensive guide unravels the concepts, methodologies, and applications of two-tailed hypotheses, providing a roadmap for researchers and students alike.
The exploration begins with an overview of hypothesis testing, delving into the types of hypotheses and their significance. The focus then shifts to two-tailed hypotheses, highlighting their unique characteristics and applications. The subsequent sections provide a step-by-step guide to designing experiments, selecting appropriate sample sizes, and employing random sampling techniques.
Hypothesis Overview

In scientific research, a hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. It is based on evidence and observation, and it can be tested through experimentation. There are different types of hypotheses, including:
- Null hypothesis (H0):This hypothesis states that there is no significant difference between two groups or variables.
- Alternative hypothesis (Ha):This hypothesis states that there is a significant difference between two groups or variables.
- Research hypothesis:This hypothesis is a more specific prediction about the outcome of an experiment.
Two-Tailed Hypothesis: An Experimenter Conducted A Two Tailed Hypothesis
A two-tailed hypothesis is a hypothesis that predicts that there will be a significant difference between two groups or variables, but it does not specify which group or variable will have the higher value. This is in contrast to a one-tailed hypothesis, which predicts that there will be a significant difference in one specific direction.
An example of a two-tailed hypothesis would be: “There will be a significant difference in the average test scores of students who study for an exam compared to students who do not study for an exam.”
Experiment Design

To design an experiment to test a two-tailed hypothesis, the following steps should be followed:
- Define the research question:What do you want to learn from your experiment?
- Formulate the hypothesis:What is your prediction about the outcome of the experiment?
- Determine the independent and dependent variables:The independent variable is the variable that you will manipulate, and the dependent variable is the variable that you will measure.
- Select the participants:Who will participate in your experiment?
- Design the experiment:How will you conduct your experiment?
- Collect the data:Gather the data from your experiment.
- Analyze the data:Use statistical methods to analyze the data from your experiment.
- Interpret the results:What do the results of your experiment mean?
Data Analysis
The statistical methods used to analyze data from an experiment with a two-tailed hypothesis include:
- t-test:This test is used to compare the means of two independent groups.
- ANOVA:This test is used to compare the means of three or more independent groups.
- Regression analysis:This test is used to determine the relationship between two or more variables.
The p-value is a measure of the statistical significance of the results of a hypothesis test. A p-value of less than 0.05 is considered to be statistically significant.
Reporting Results

When writing a scientific report that includes the results of a two-tailed hypothesis test, the following information should be included:
- The research question
- The hypothesis
- The methods
- The results
- The discussion
- The conclusion
The results section should include the statistical analysis that was used, the p-value, and the interpretation of the results.
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of a two-tailed hypothesis?
A two-tailed hypothesis allows researchers to test whether there is a significant difference between two groups in either direction, without specifying a predicted direction.
How do you determine the appropriate sample size for a two-tailed hypothesis test?
The appropriate sample size depends on the desired level of statistical power, the effect size, and the variability of the data.
What is the difference between a p-value and a significance level?
The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as or more extreme than the observed statistic, assuming the null hypothesis is true. The significance level is the predetermined threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis.