The history of the atom worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the groundbreaking discoveries and theories that have shaped our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of matter. From the early speculations of ancient Greek philosophers to the cutting-edge advancements of modern physics, this worksheet traces the evolution of atomic theory, offering a captivating account of scientific progress.
Through engaging activities and thought-provoking questions, this worksheet invites learners to explore the milestones and key figures that have contributed to our current understanding of the atom. By delving into the history of atomic theory, students gain a deeper appreciation for the scientific process and the ever-evolving nature of our knowledge about the universe.
1. Introduction
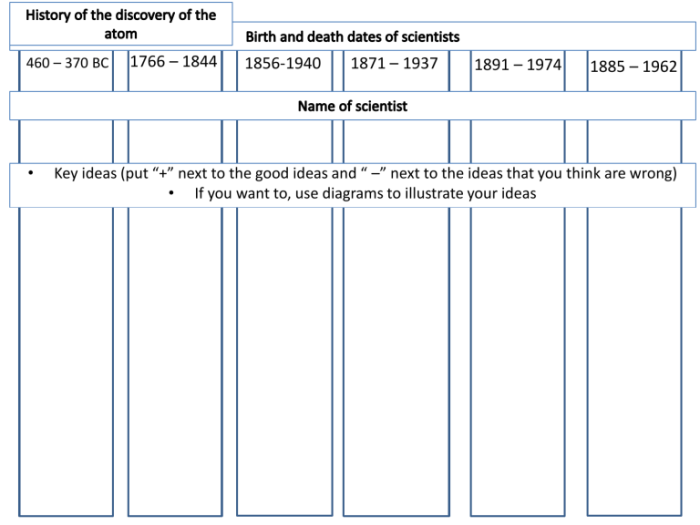
The history of the atom is a fascinating journey that has led to a profound understanding of the fundamental nature of matter. From the early speculations of ancient philosophers to the groundbreaking discoveries of modern science, this history has been marked by key milestones and discoveries that have shaped our understanding of the atom.
2. Early Theories of Matter: The History Of The Atom Worksheet
The ancient Greek philosophers, such as Democritus and Aristotle, proposed various ideas about the composition of matter. Democritus’ atomic theory, which proposed that all matter is composed of indivisible particles called atoms, had a significant influence on scientific thought.
Aristotle’s Opposing Views
Aristotle, however, held opposing views, arguing that matter was continuous and could be divided indefinitely. His ideas dominated scientific thought for centuries, hindering the development of atomic theory.
3. The Development of Chemical Atomic Theory
In the 19th century, John Dalton proposed his atomic theory, which laid the foundation for modern chemistry. This theory proposed that elements are composed of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms, each with a unique atomic weight.
Contributions of Avogadro and Berzelius
Amedeo Avogadro’s hypothesis on the nature of gases and Jöns Jakob Berzelius’ work on atomic weights further refined and expanded Dalton’s theory, leading to a deeper understanding of atomic structure.
4. The Discovery of Subatomic Particles
The discovery of the electron by J.J. Thomson in 1897 marked a turning point in the understanding of the atom. This discovery showed that atoms were not indivisible and that they contained smaller, negatively charged particles.
Rutherford’s Gold Foil Experiment, The history of the atom worksheet
Ernest Rutherford’s gold foil experiment in 1911 further revealed the structure of the atom. This experiment showed that most of the atom’s mass was concentrated in a small, positively charged nucleus, surrounded by orbiting electrons.
Bohr’s Planetary Model
Niels Bohr’s planetary model of the atom, proposed in 1913, refined Rutherford’s model by suggesting that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific, quantized energy levels.
5. The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
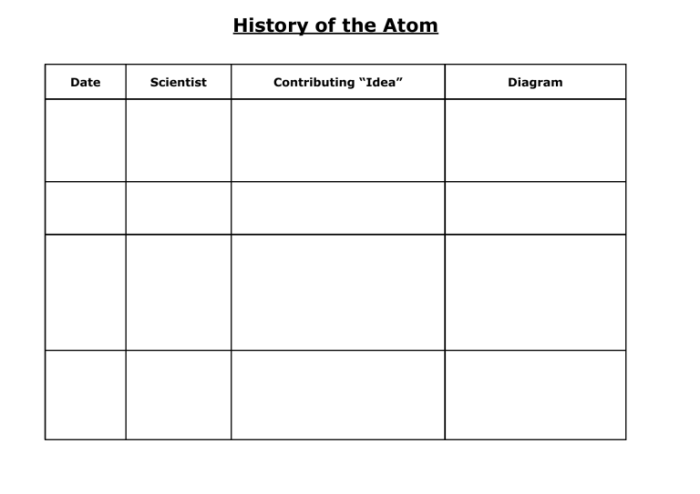
The development of quantum mechanics in the early 20th century revolutionized our understanding of the atom. The wave-particle duality of electrons and the uncertainty principle introduced new concepts that challenged the classical view of the atom.
Contributions of Schrödinger, Heisenberg, and Born
Erwin Schrödinger’s wave equation, Werner Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, and Max Born’s probabilistic interpretation of the wave function were key contributions to the development of the quantum mechanical model of the atom.
6. Modern Atomic Theory
The modern atomic theory, based on quantum mechanics, provides a comprehensive understanding of the atom. It describes the structure of the nucleus, the arrangement of electrons in energy levels, and the behavior of atoms in chemical reactions.
Periodic Table and Applications
The periodic table, organized based on atomic number and electron configuration, reflects the properties and behavior of elements. Atomic theory has wide-ranging applications in chemistry, physics, and materials science, providing a foundation for understanding the structure and properties of matter.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the key milestones in the history of atomic theory?
Key milestones include Democritus’ atomic theory, Dalton’s atomic theory, the discovery of the electron, Rutherford’s gold foil experiment, Bohr’s planetary model, and the development of quantum mechanics.
Who are some of the major contributors to the development of atomic theory?
Major contributors include Democritus, John Dalton, J.J. Thomson, Ernest Rutherford, Niels Bohr, Erwin Schrödinger, Werner Heisenberg, and Max Born.
How has the understanding of the atom changed over time?
The understanding of the atom has evolved from the indivisible particles proposed by Democritus to the complex quantum mechanical model we have today, which includes subatomic particles like electrons, protons, and neutrons.
