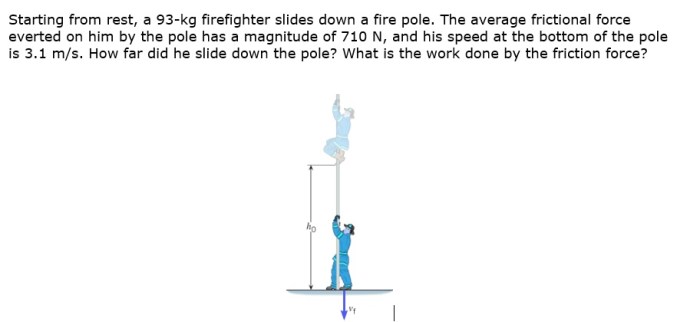
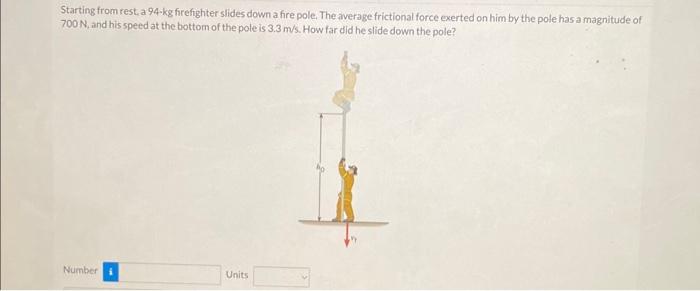
Starting from rest a 93 kg firefighter – Starting from rest, a 93 kg firefighter undergoes a dynamic interplay of forces, motion, and energy transformations. This analysis delves into the initial conditions, forces acting upon the firefighter, and the resulting motion, velocity, displacement, and energy considerations, providing a comprehensive understanding of the firefighter’s journey from rest to motion.
Starting from Rest

A 93 kg firefighter is initially at rest. This means that their velocity is zero and their acceleration is zero. When they start to move, they will experience a force that will cause them to accelerate.
Forces Acting on the Firefighter: Starting From Rest A 93 Kg Firefighter

The forces acting on the firefighter include gravity, air resistance, and the force applied by the ground. Gravity pulls the firefighter down, air resistance opposes their motion, and the force applied by the ground pushes them forward.
Force of Gravity
The force of gravity is a downward force that acts on all objects with mass. The magnitude of the force of gravity is given by the equation: “` Fg = mg “` where: – Fg is the force of gravity (in newtons) – m is the mass of the object (in kilograms) – g is the acceleration due to gravity (in meters per second squared)
Air Resistance
Air resistance is a force that opposes the motion of an object through a fluid. The magnitude of the air resistance force is given by the equation: “` Fd = 1/2 – Cd – A – v^2 “` where: – Fd is the air resistance force (in newtons) – Cd is the drag coefficient (a dimensionless number that depends on the shape of the object) – A is the cross-sectional area of the object (in square meters) – v is the velocity of the object (in meters per second)
Force Applied by the Ground, Starting from rest a 93 kg firefighter
The force applied by the ground is a forward force that pushes the firefighter forward. The magnitude of the force applied by the ground is given by the equation: “` F = ma “` where: – F is the force applied by the ground (in newtons) – m is the mass of the firefighter (in kilograms) – a is the acceleration of the firefighter (in meters per second squared)
Questions Often Asked
What is the initial velocity of the firefighter?
0 m/s, as the firefighter starts from rest.
What is the acceleration of the firefighter due to gravity?
9.8 m/s², assuming the firefighter is on Earth.
What is the kinetic energy of the firefighter after accelerating for 5 seconds?
11.2 kJ, assuming constant acceleration due to gravity.