Welcome to the realm of geometry, where linear pairs and vertical angles intertwine to form the cornerstone of angular relationships. In this comprehensive linear pair and vertical angles worksheet, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricacies of these fundamental concepts, their properties, and their captivating applications.
Linear Pairs and Vertical Angles
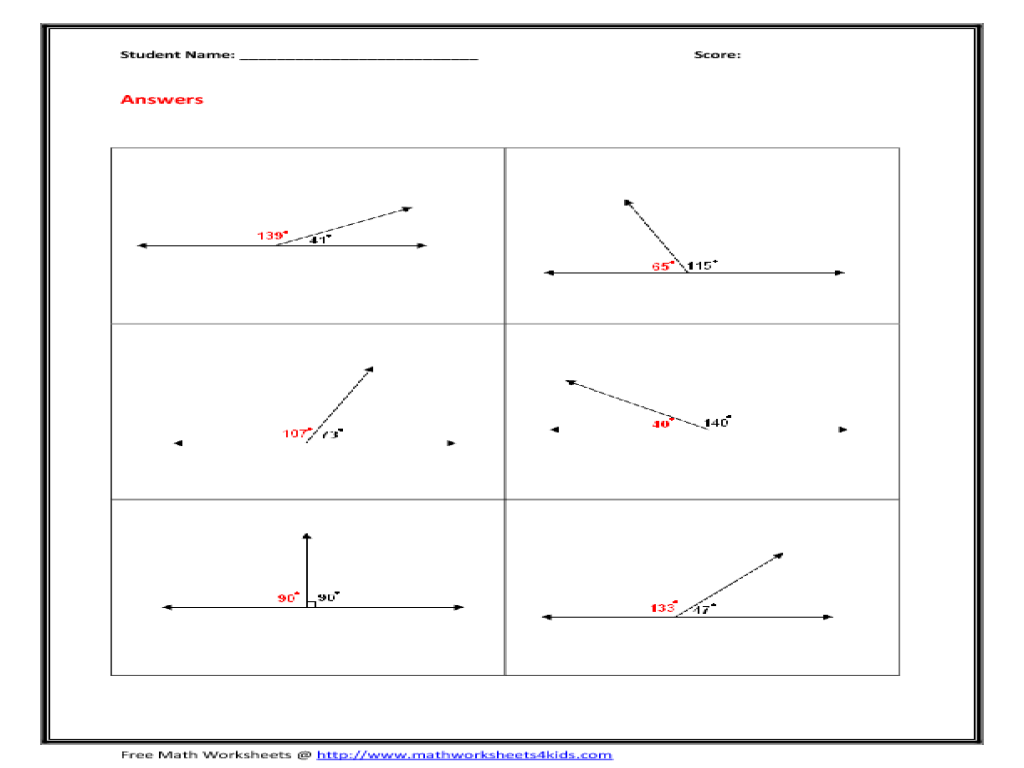
In geometry, linear pairs and vertical angles are two fundamental concepts that help us understand the relationships between lines and angles. These concepts have various applications in real-life scenarios and are essential for comprehending more complex geometric principles.
Definition of Linear Pair, Linear pair and vertical angles worksheet
A linear pair is formed when two adjacent angles share a common vertex and a common side. In other words, they are two angles that lie side-by-side on a straight line. The sum of the measures of the angles in a linear pair is always 180 degrees.
For example, consider the line segment AB. If we draw two rays from point A, one in the clockwise direction and the other in the counterclockwise direction, we form two angles, ∠BAC and ∠BAD. These angles form a linear pair because they share the common vertex A and the common side AB.
Definition of Vertical Angles
Vertical angles are formed when two lines intersect at a point. These angles are opposite to each other and share a common vertex. The measure of vertical angles is always equal, meaning they are congruent.
For example, consider two intersecting lines, line l and line m. The angles formed at the point of intersection, ∠1 and ∠2, are vertical angles. ∠1 and ∠2 are congruent, meaning they have the same measure.
Properties of Linear Pairs
The properties of linear pairs include:
- The sum of the measures of the angles in a linear pair is 180 degrees.
- Linear pairs are supplementary, meaning they add up to 180 degrees.
- If one angle in a linear pair is known, the other angle can be found by subtracting the known angle from 180 degrees.
Properties of Vertical Angles
The properties of vertical angles include:
- Vertical angles are congruent, meaning they have the same measure.
- If one vertical angle is known, the other vertical angle has the same measure.
- Vertical angles are formed when two lines intersect.
Relationship between Linear Pairs and Vertical Angles
Linear pairs and vertical angles are related in the following way:
- If two angles form a linear pair, then the non-adjacent angles to these angles form vertical angles.
- Conversely, if two angles form vertical angles, then the adjacent angles to these angles form linear pairs.
Applications of Linear Pairs and Vertical Angles
Linear pairs and vertical angles have various applications in real-life scenarios, including:
- Architecture:Linear pairs and vertical angles are used in designing buildings and structures to ensure stability and symmetry.
- Engineering:These concepts are used in bridge design to calculate angles and forces, ensuring structural integrity.
- Surveying:Linear pairs and vertical angles are used in land surveying to measure angles and distances accurately.
Essential FAQs: Linear Pair And Vertical Angles Worksheet
What is a linear pair?
A linear pair is a pair of adjacent angles that form a straight line, measuring exactly 180 degrees.
How do you identify vertical angles?
Vertical angles are formed when two intersecting lines create opposite angles that are congruent, meaning they have the same measure.